Today’s big companies have complex portfolios of businesses and brands. Creating strategic and marketing plans for such business portfolios can be challenging but essential.
The main task in strategic planning is business portfolio analysis which determines which businesses should receive more, less, or no investment.
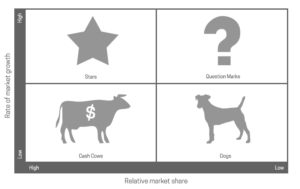
The Boston Consulting Group approach – also known as the Boston matrix or Growth-share matrix is the most renowned corporate portfolio analysis tool. It helps the company evaluate strategic business units (SBUs) on two important dimensions: growth and relative market share.
The company with the BCG matrix can phase down or drop some businesses or products that have no greater return than others and can invest more in its more profitable businesses.
According to the BCG matrix, businesses can be classified as high or low according to their industry growth rate and relative market share.
On the vertical axis, the market growth rate provides a measure of market attractiveness. On the horizontal axis, relative market share serves as a measure of company strength in the market.
BCG portfolio matrix defines four types of SBUs: Question marks, Cows, Dogs, and Stars
Stars: Stars are considered businesses or products with a high market share in a fast-growing industry.
They generate large among of cash along with requiring significant investment to remain successful and maintain a competitive advantage. Monopolies and first-to-market products are usually known as stars.
Eventually, their growth slows down, and they will turn into cash cows.
A Coca-Cola product, Kinley is an example of a star. The mineral water industry is still viewed as a gradually growing market and fulfills the needs of people. The need for bottled water has not decreased which is why the growth opportunities for this product are high.
Cash cows: In the market, there are products whose market growth decreased but still hold a high market share.
Cash cows are mature and need less investment to maintain their position. They generate high cash flow that is generally used to finance stars or question marks that need investment.
Apple’s Macbook has a consistent market share and steady revenue, making it a cash cow for the company.
Question marks: question marks are these products that are in growing marketing but have low market share.
They require a large amount of cash to maintain and gain market share and deliver little return for the company.
But question marks may have potential growth in the future that can turn into a star. That is why companies are advised to invest in question marks.
Coca-cola’s product, Fanta can be an example of question marks. The brand has not been able to be not as popular as Coke. But in some markets, it has been able to gain high sales volume.
Dogs: Dogs are low-growth, low-share businesses, and products. They are typically able to generate enough cash flow to remain in the market but they never turn into stars.
For Companies, dogs are generally prime candidates for divestiture unless the products are complementary to existing products or are used for competitive purposes.
Diet coke is considered a dog product of Coca-Cola. Diet Coke is in the market to offer consumers healthier drink options in terms of calories consumed. But, it has not captured consumers’ interest enough, and therefore its sales have declined. The company does not see growth potential.
Final Thoughts
Once the company has classified its SBUs, it must evaluate what role each will play in the future. They can follow one of four strategies for each SBU.
The company can spend more cash on the product to increase its share. Or they can invest just enough to hold the SBU’s share at the current level. They can harvest the SBU, milking its short-term cash flow regardless of the long-term effect.
Finally, they can get rid of the SBU that does not deliver a good return.
As needed consider, that SBUs change their positions in the growth-share matrix.
At first, many SBUs become question marks and turn into star categories if they succeed. Later they become cash cows as market growth decreases and then finally move into dogs toward the end of the life cycle